What is cortisone?
Cortisone is a type of medication that reduces inflammation. It belongs to a larger group of steroid hormones known as glucocorticoids. Cortisone is closely related to cortisol, a natural substance produced by our bodies. During times of stress, the adrenal glands produce cortisol, which travels in the bloodstream and acts over a short period of time. Cortisone is a synthetic version of cortisol that acts more potently over an extended period of time.
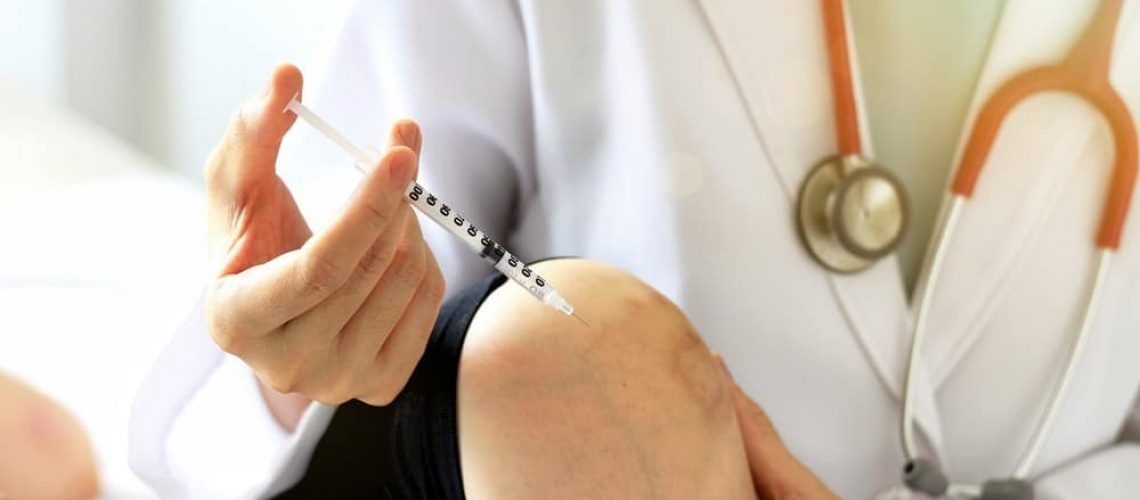
How do healthcare providers administer cortisone?
Medical professionals often administer cortisone via injection. Patients can also use cortisone orally or topically.
How does cortisone work in our bodies?
Physicians use cortisone to reduce localized areas of inflammation in our bodies such as knee, shoulder, and elbow joints. Cortisone decreases swelling, which often diminishes pain and discomfort. Providers usually mix cortisone with a local anesthetic upon injection. This local anesthetic enables patients to experience more immediate pain relief up to several hours. Although cortisone acts over a longer period of time, it can take up to two weeks to affect the inflamed site.
What is cortisone used to treat?
Cortisone is not a direct pain-relieving medicine. Instead, cortisone reduces inflammation, which is caused by various conditions such as bursitis, tendinitis, and osteoarthritis. Cortisone can also be used to treat trigger finger and gout.
Does cortisone work?
While each person can experience different results from a cortisone injection, many patients report pain-relieving effects lasting from several weeks to several months. However, an excessive quantity of cortisone exposure can damage the joint cartilage. Thus, physicians usually recommend that no more than three cortisone injections be administered to the affected body part each year.